Your home’s electrical system relies heavily on circuit breakers to protect you from potential hazards like electrical overloads, short circuits, and other malfunctions. However, over time, even circuit breakers can wear out. Recognizing a faulty breaker early can save you from expensive repairs and prevent more serious risks, such as electrical fires.
In this guide, we’ll help you identify the common signs of a bad circuit breaker, explain how to test it, and show you how to replace it if necessary. Let’s dive into how to spot those early warning signs and act quickly to keep your electrical system functioning safely.
Signs Your Circuit Breaker Might Be Failing
Frequent Tripping
If your circuit breaker keeps tripping often, it’s a clear indication that something’s wrong. Frequent tripping could point to:
- Overloaded Circuit: Too many devices on a single circuit.
- Short Circuit: Wires have become damaged, causing an unintended electrical path.
- Ground Fault: Electrical current is flowing outside its intended path, which can lead to dangerous situations.
If your breaker trips often, it’s time to have it checked by a professional.
Breaker Won’t Stay in the “ON” Position
A breaker that flips back to “OFF” after being reset is usually a sign of internal failure. Possible causes include:
- Damaged Components: The breaker’s internal parts are worn out.
- Faulty Connections: Loose or incorrect wiring can cause the breaker to malfunction.
Burning Smell or Scorched Marks
If you smell something burning near the breaker panel, this is a serious concern. It often means that the breaker is overheating due to:
- Excessive Current: The breaker is overloaded.
- Damaged Insulation: The wires have deteriorated, causing heat buildup.
Visible scorch marks around the breaker are another red flag that the breaker is struggling to handle the power flow.
Unusual Sounds
Buzzing, crackling, or humming noises coming from the breaker panel can indicate trouble. These sounds often come from:
- Loose Connections: Wires that aren’t securely connected can cause arcing.
- Electrical Arcing: This occurs when electricity jumps between contacts, which is a serious fire risk.
If you hear any strange sounds, it’s best to call a licensed electrician immediately.
Breaker Box Feels Warm or Hot
If your breaker panel feels warm or hot to the touch, something’s likely wrong. Possible causes include:
- Overloaded Circuits: Too many devices drawing power from a single breaker.
- Faulty Breaker: The breaker may have internal issues preventing it from properly regulating the electricity.
An overheated breaker panel is a potential fire hazard, so it’s important to act quickly.
Flickering or Dimming Lights
If your lights are flickering or dimming unexpectedly, it could be a sign of a bad breaker. Causes include:
- Loose Wiring: Faulty connections inside the breaker panel.
- Overloaded Circuits: Too many devices on a single circuit could cause a voltage drop.
If this happens, it’s important to investigate before the problem worsens.
Visible Wear or Physical Damage
Circuit breakers are designed to last, but over time, wear and tear can take a toll. If you see cracks, scorch marks, or other signs of physical damage, it’s time to replace the breaker.
Types of Circuit Breakers
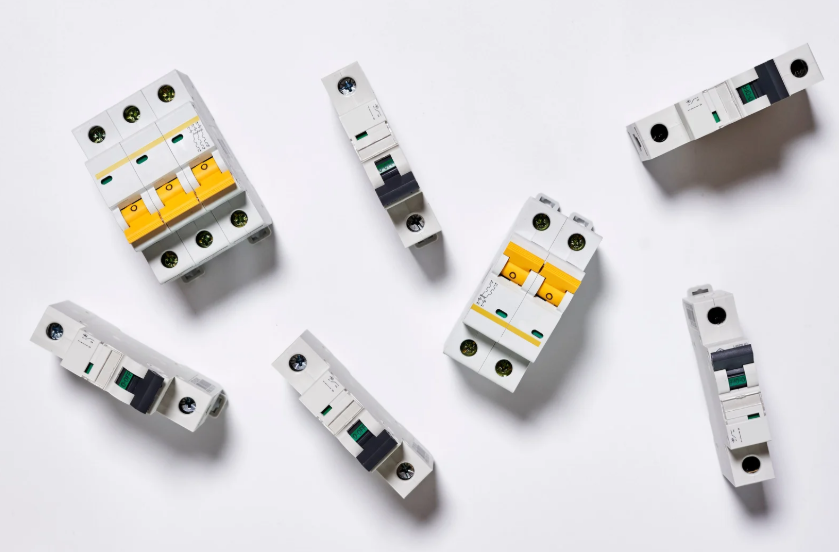

Before diving into testing and troubleshooting, it’s important to understand the types of circuit breakers you might have in your electrical panel:
- Single-Pole Breakers: Common in standard 120V circuits for everyday appliances.
- Double-Pole Breakers: Used for 240V circuits, typically for large appliances like ovens or dryers.
- Ground Fault Circuit Interrupter (GFCI) Breakers: Protects against electrical shocks by detecting ground faults, typically used in wet areas like bathrooms or kitchens.
- Arc Fault Circuit Interrupter (AFCI) Breakers: Designed to prevent fires by detecting arcing faults.
Understanding which type of breaker you have will help you identify the root cause of problems more effectively.
Common Causes for Breaker Failures
While many factors can cause circuit breakers to fail, some common causes include:
- Aging Components: As breakers age, their internal mechanisms degrade, leading to malfunctions.
- Electrical Overload: A common cause of trips, especially in homes with a high electrical demand.
- Improper Installation: Breakers that are installed incorrectly may malfunction or fail prematurely.
- Environmental Factors: Dampness, heat, or physical damage to the breaker panel can shorten a breaker’s lifespan.
How to Test if Your Circuit Breaker is Bad
If you suspect your breaker is faulty, here’s how you can test it:
Visual Inspection
Start by visually inspecting the breaker for any signs of damage like scorch marks, cracks, or a burning smell.
Multimeter Testing
Use a multimeter to check the voltage of the breaker:
- Set the multimeter to measure AC voltage.
- Place the probes on the breaker terminals.
- If the reading is zero or inconsistent, the breaker might be bad.
Continuity Test
Turn off the breaker and check for continuity. If there’s no continuity, the breaker may be defective.
Breaker Swap Test
If you have a spare breaker, swap it out with the faulty one. If the issue persists, the problem may be with the wiring or the circuit, not the breaker itself.
How to Replace a Faulty Circuit Breaker
If your breaker is beyond repair, replacing it is straightforward:
- Turn Off the Main Power: For safety, turn off the main power supply to the breaker box.
- Remove the Faulty Breaker: Unscrew and disconnect the wires from the defective breaker.
- Install the New Breaker: Attach the wires to the new breaker, secure it in place, and ensure everything is connected properly.
- Turn On the Power: Once everything is in place, turn the power back on and test the new breaker to ensure it’s working.
If you’re unsure, don’t hesitate to call a licensed electrician.
What to Do if You Suspect a Faulty Circuit Breaker
- Turn Off the Power: Safety should always come first. If you notice any issues with a breaker, switch off the power to the affected circuit.
- Check for Obvious Damage: Look for signs like burn marks or melted wires, which suggest the breaker needs replacing.
- Call a Professional: If you’re unsure about diagnosing or replacing the breaker, contact a licensed electrician to ensure everything is handled properly.
- Replace the Breaker: If you’re comfortable with electrical work, you can replace the breaker yourself. However, if you’re uncertain, it’s safer to hire a professional.
When to Call a Professional
While replacing a circuit breaker yourself is an option, certain situations require the expertise of a licensed electrician:
- Persistent Issues: If the breaker keeps tripping with no clear cause.
- Visible Damage: If there are burn marks or melted parts.
- Flickering Lights: If lights frequently flicker or dim.
- Burning Smell: A burning odor near the breaker panel.
- Overheating Panel: If the breaker panel feels hot to the touch.
Electrical work can be dangerous, so if you’re in doubt, always call in a professional.
How Long Do Circuit Breakers Last?
Circuit breakers typically last between 30 to 40 years, depending on usage and environmental factors. However, frequent electrical surges, overloads, or poor installation can shorten their lifespan. If you live in an older home or notice signs of wear, it might be time to replace the breaker, even if it hasn’t fully failed yet.
Final Thoughts
Circuit breakers play a crucial role in keeping your home’s electrical system safe. Being able to spot the signs of a bad breaker can help prevent larger electrical problems down the line. Regular inspections, early detection, and timely replacements are key to maintaining a safe and reliable electrical system. Don’t wait—if you notice any warning signs, consult a professional to keep your home secure.
Frequently Asked Questions
Can a circuit breaker go bad without tripping?
Yes, it’s possible. Some issues, like internal damage, may prevent the breaker from tripping even when it should.
How often should I replace a circuit breaker?
Circuit breakers typically last 30 to 40 years, but it’s a good idea to inspect and maintain them regularly.
What causes a circuit breaker to trip?
Overloaded circuits, short circuits, and ground faults are common causes.
How can I prevent circuit breaker problems?
Avoid overloading circuits, inspect your electrical system periodically, and schedule professional inspections every few years.